(1) Introduction

The Japan Plant Variety Protection and Seed Act has been established to protect new plant varieties. In order to register a new plant variety, it is necessary to file a registration application with the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF).
"The holder of the breeder's right", who has obtained the breeder's right of a new plant variety by registration, has an exclusive right to (i) exploit the registered plant variety in the course of business (e.g., cultivation, sale, etc. of plants) and (ii) circulate the variety in the market under its registered name without interference by the third parties. If another person who has no permission exploits plants, crops, etc. of a registered variety in the course of business, the exploitation constitutes an infringement of the breeder's right. In such a case, the holder of the breeder's right can demand injunction of that exploitation and/or compensation for damages caused by that infringement.
It is not easy to categorize various plant varieties based solely on their appearances, and therefore each plant variety is mainly identified by its name. Under the circumstances, registration of plant varieties is recognized for the purpose of standardization and smoothing of distribution and exploitation of plants.

Registered plant varieties are protected for 25 years from the date of registration (in the case of perennial plants such as fruit trees, lumber trees, etc., the period of protection is 30 years).
*The duration of right may differ depending on the date of registration because the old Plant Variety Protection and Seed Act may be applied.
Plant variety registration is an important system for protecting your valuable plant varieties from imitation and unauthorized exploitation both in Japan and abroad.
As with other intellectual property rights, the jurisdiction for plant variety registration is based on the territoriality principle, and registration must be made in every country where protection is desired. In recent years, the unauthorized outflow of Japanese plant varieties abroad, particularly to East Asian countries, has been a big issue. Under the circumstance, MAFF finally announced "Emergency Measures for Prevention of Outflow of Plant Varieties Abroad", promoting awareness of the plant variety registration system.
This page is intended to support intellectual-property-related activities of those who are engaged in the agricultural industry.
(2) Container Design Helps to Draw Attention to Agricultural Product
In order to protect your agricultural product as an intellectual property, we propose using, for example, the "plant variety registration (with breeder's right)" under the Plant Variety Protection and Seed Act, the "trademark right" under the Trademark Act, and/or the "patent right" under the Patent Law.
Specially, combination of the plant variety registration and the trademark registration is very important to promote and defend brand values. (For more details about combination of the Plant Variety Protection and Seed Act and the Trademark Act, see this article)
- Other than the above solutions, how do you promote and defend brand values of agricultural products?
• Using a unique design for the wrapping, the selling space, etc. will make it possible to differentiate your product from other's.
• Strengthening the concept of the design and continuing to sell your product with a single design will make it possible to cause the consumers to strongly remember the variety and/or brand.
However, unlike patents that cannot be imitated at a glance, it is easy for another person to imitate your design at a glance because designs are "visible features". This is the weak point of designs.
"Design Right" is a right that protects your design and allows you to exclusively use your design so that nobody can imitate your design.
The following examples are agricultural-product-related designs that have been registered in Japan.
Decoration for Strawberry
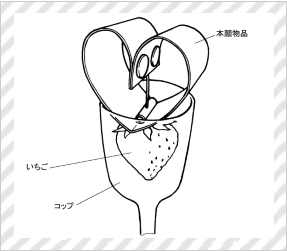
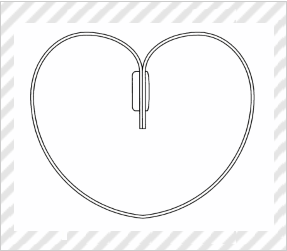
(Ichigo Company Inc., Design Registration No. 1538672)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The article to the claimed design is made of a thin resin plate, and is used to serve a strawberry to a table in such a manner that the strawberry is hanged from the article placed on a glass.
Wrapping Bag


(Pacific Around Inc., Design Registration No. 1464511)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The claimed article is a wrapping paper bag for storing, for example, two cups of rice.
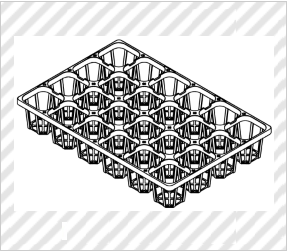
Case for Displaying Commodity
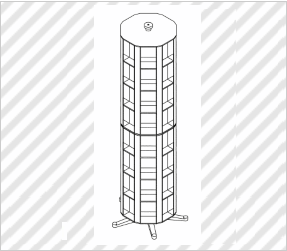
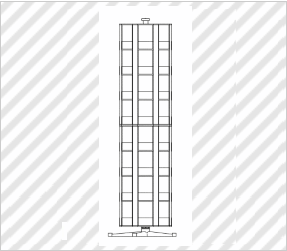
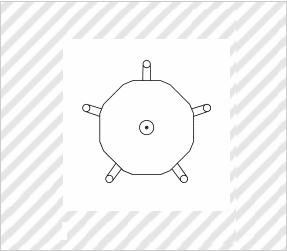
(Atariya Farm Corp., Design Registration No. 1350675)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The claimed article is mainly used to sell, as commodities, seeds that are packed in bags, and displays the commodities by storing a plurality of commodities in each rectangular space.
Container for Strawberry
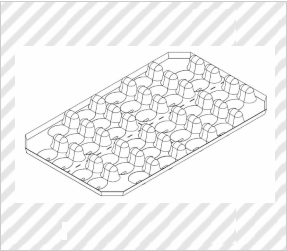
(DOÑANA 1998 S.L., Design Registration No. 1566618)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The claimed article is a container for transportation and storage of fruits, particularly strawberries.
(3) Design Can Be Protected Not Only Entirely But Also "Partially"
The design system is intended basically to protect the design of an entire article. It follows that, in a case where (i) your registered design has a characteristic in a specific portion and (ii) a third party exploits a design which imitates that portion of your registered design but is not entirely similar to your registered design, the efficacy of your design right will not reach the exploitation by the third party.
In order to avoid such an exploitation, it is possible to register not only an entire design but also part of a design as a "partial design". This makes it possible obtain a design right whose scope is limited to the characteristic portion of your design.
The following examples are agricultural-product-related "partial designs" that have been registered in Japan. (Solid lines indicate the scope of each partial design.)
Container for Wrapping (Partial Design)
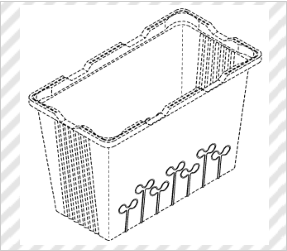
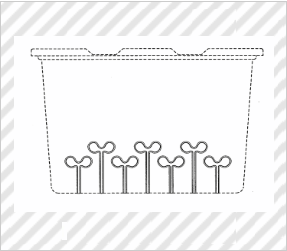
*Solid lines indicate the scope of the partial design.
(Mamoru KAMO, Design Registration No. 1307118)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The article to the design is formed by swelling and molding a synthetic resin sheet material, and is a container for wrapping mainly vegetable sprouts such as radish sprouts, broccoli sprouts, and mustard sprouts.
Combine-harvester (Partial Design)

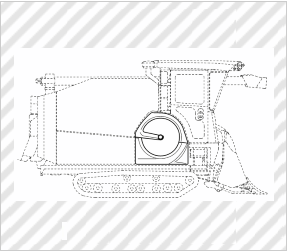
*Solid lines in the plan view indicate the scope of the partial design.
(YANMAR CO., LTD., Design Registration No. 1440568)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
A portion, to be registered as a design, of the combine-harvester to the claimed design is a rotary screen that covers the engine room for supplying external air to the engine room.
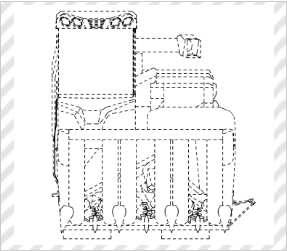
Tray for Storing Seedling-raising Pots
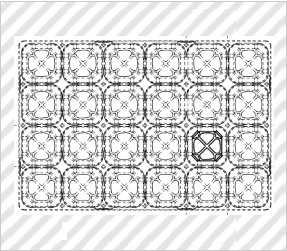
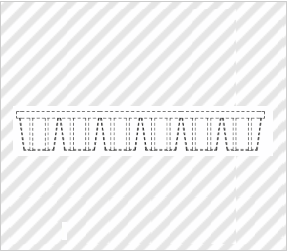
*Solid lines indicate the scope of the partial design.
(Forza Corporation., Trademark Registration No. 1562011)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The claimed article is a tray for storing seedling-raising pots which tray includes a given number of recesses that are arranged vertically and horizontally. Each recess has an identical frame structure in which (i) each side of a bottom surface, which has a substantially square shape when viewed from above, and (ii) a corresponding side of an upper opening, which is greater than the bottom surface and has a substantially square shape when viewed from above, are connected via two flat connection plates, and stores a single pot. In the frame structure, (i) the bottom surface of each recess has four large openings, each having a teardrop shape when viewed from above, which are arranged between sides of a flat plate frame, extending along diagonal lines, which has a cross shape when viewed from above, and (ii) four small openings, each of which is surrounded by adjacent large openings and a corner portion, are provided. The design is therefore symmetric with respect to a point.
(4) Surprising Examples of Registered Design
Other than the above articles related to circulation or sale of agricultural products, articles that are necessary for cultivating agricultural products are also protected under design right.
Please refer to the following examples.
Frame for Plastic Greenhouse (Partial Design)
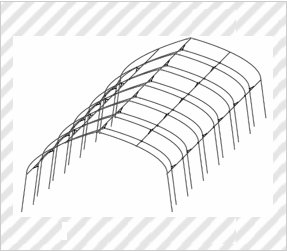
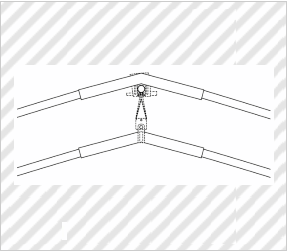

*Solid lines indicate the scope of the partial design.
(KOSHIURAPIPE Inc., Design Registration No. 1507189)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The claimed article is a frame for a plastic greenhouse having a double-arch structure.
Circulation Air Blower for Plastic Greenhouse
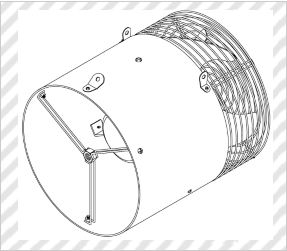
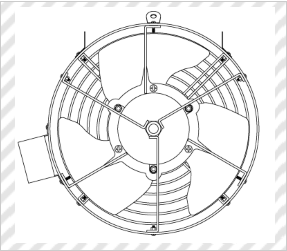
(Variteck Nigata, Design Registration No. 1194284)
[Explanation of Article to Design]
The claimed article is to be provided in a plastic greenhouse for circulating air in the plastic greenhouse while the plastic greenhouse is closed. It has a multi-purpose supporter to which an ejector of water, chemicals, or Co2 gas, a lamp, etc. can be attached.
(5) "HARAKENZO more " assist those who are engaged in the agricultural industry.
In selling agricultural products or products processed therefrom, differentiating your products from competitor's products by using a unique design is strategically important. Meanwhile, if your design is not appropriately protected as an intellectual property, another person can easily circulate imitations of that design in the market, which will make you busy taking measures against those imitations.
In contrast, if you create a design and exploit the design without making a search on registered designs etc., it may infringe somebody's design right and, in the worst-case scenario, you may be sued for that infringement.
As described above, you may face situations where you have no other choice but to take some measures for intellectual-property-related problems. "HARAKENZO more " are all prepared for taking our utmost effort to protect your intellectual properties. Please feel free to contact us.
意匠の疑問・お悩みはHARAKENZOに相談ください!

意匠登録や意匠トラブルの解決にあたっては、専門家の判断が欠かせません。
意匠のことでお悩みがありましたら、いつでも知的財産のプロフェッショナル集団であるHARAKENZO事務所にご相談いただけます。
