(1) Introduction
It can be said that toys are fantastic tools which form one’s childhood as one poet describes in his work: “toys are the child’s first initiation into art, or rather, it is the first concrete example of art.” The toys are still attractive even for adults, and have depth which does not allow us to call the toys “merely tools to play with.” Meanwhile, it is said that toys for babies also play an important role of intellectual training and education which enrich sentiment and sociality of the babies.
In recent years, the domestic market of the toy industry in Japan has been slightly shrinking due to an issue of a declining birthrate, influence brought about by, for example, change and diversification of consumer preference, and tendency of the whole toy industry to depend on the trend of the society. However, in 2014, the toy industry recorded the biggest sales in the last 10 years in the domestic market due to, for example, explosive hit of “YO-KAI WATCH,” a boom of “FROZEN,” and sales of toys collaborated with the opening of Hokuriku Shinkansen. Thus, the toy industry recovers its vitality, and now exhibits its strong potential power. In the future, demands for toys integrated with high technologies, revival of analog toys, and toys for elderlies are expected to arise.
"HARAKENZO more " have prepared this web page to support intellectual property activities of those in the toy industry which supports Japan. We hope this web page benefits those who are considering to file a design application.
(2) Designs for toys
How to attract and fascinate general consumers is very important for toys. In particular, intuitive attractive impression is still more important for toys for children. One of important factors which determine the impression of a toy is a “design.” A good design for the toy will be regarded as a “symbol” of a maker of the toy in the public.
However, the design is an “external feature” which can be seen through the eye, and there is a strong possibility that, unlike a patent technology which is difficult to be imitated at a glance, the design is easily imitated at a glance. This is a weakness of the design.
A “design right” protects such a easily imitated design so as to allow a design right holder to exclusively use the design and prevent other people from imitating the design.
The following examples are design rights obtained by Japanese toy makers.
★Spinning top


Group E (Hobby and Recreation Goods and Athletic Implements)
(TOMY COMPANY, LTD., Design Registration No. 1538616)
★Transforming toy
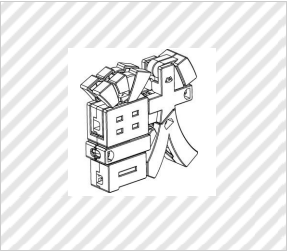
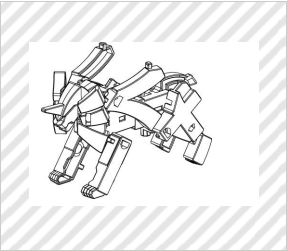
Group E (Hobby and Recreation Goods and Athletic Implements)
(BANDAI CO., Ltd., Design Registration No. 1453138)
★Doll house

Group E (Hobby and Recreation Goods and Athletic Implements)
(EPOCH CO., LTD., Design Registration No. 1449207)
(3) “Partial design” is also protectable
A design right covers a design for a whole article. However, the design right for the whole article does not protect a design for a part of the article (partial design) having a feature. That is, in a case where a third person imitates a partial design for your toy, and produces a toy which has the imitated partial design but a whole design for the toy of the third person is not similar to a design for your toy, your design right for your whole toy cannot prevent the third person from using the partial design.
In order to avoid such a situation, it is possible not only to register the whole design for the toy, but also to register the “partial design” for the toy. Accordingly, if your toy has a partial design having a feature, it is possible to obtain a design right limited to the partial design.
The following examples are partial design rights obtained by Japanese toy makers (in the following drawings, solid lines illustrate ranges protected by partial design rights).
★Game machine
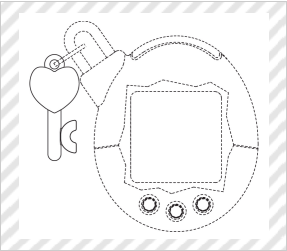
Group E (Hobby and Recreation Goods and Athletic Implements)
(BANDAI CO., Ltd., WiZ CO., LTD., Design Registration No. 1325908)
★Stuffed toy
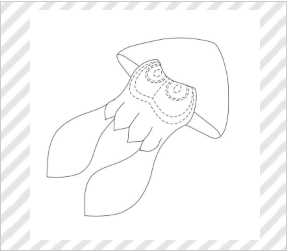
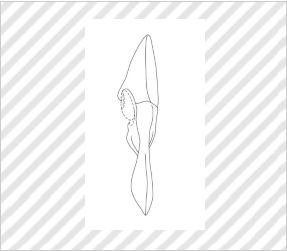
Group E (Hobby and Recreation Goods and Athletic Implements)
(Nintendo Co., Ltd., Design Registration No. 1515141)
★Wristwatch type toy (a partial design right covers a part other than a light-red-colored part)

Group E (Hobby and Recreation Goods and Athletic Implements)
(BANDAI CO., Ltd., Design Registration No. 1541881)
(4) Model toys (cars and Shinkansen etc.)
A design right basically protects “one design for one article.” In particular, for example, if a “design for Lamborghini” is protected for an “article of cars,” the “design for Lamborghini” is not protected for other articles.
Designs for cars and Shinkansen are often directly employed in toys such as model toys. If a car maker only obtains a design right for Lamborghini for the article of cars, and the other toy maker sells a toy car based on the “design for Lamborghini,” the design right obtained by the car maker does not cover the toy car (note here that, it is possible to prevent such a case with other laws such as the Unfair Competition Prevention Act).
Accordingly, in many cases, design right holders for cars also obtain design rights for “the article of toy cars.”
★ Examples of cars
(Lamborghini)


[18. Design Registration No. 1487744]Car:Automobile Lamborghini S.p.A.
[17. Design Registration No. 1487745]Toy car:Automobile Lamborghini S.p.A.
(MASERATI)


[12. Design Registration No.1328317]Car:MASERATI SPA
[13. Design Registration No. 1321556]Toy car:MASERATI SPA
★ Example of Shinkansen (East Japan Railway Company)


[44. Design Registration No. 1510220]train:East Japan Railway Company
[38. Design Registration No. 1513091]Toy train:East Japan Railway Company
Japan Railway Companies protect designs for Shinkansen for both of “the article of trains” and “the article of toy trains.”
If you consider to produce and sell a toy with a design for a vehicle such as a car or Shinkansen, it is necessary not to infringe a design right since, in many cases, a maker of the car or Shinkansen has already obtained a design right for its toy.
(5) It is too late to take measures when imitation product has appeared on the market abroad
Once a toy is in vogue in the toy industry, in some cases, an imitation product of it come into Japan from overseas (especially from East Asia), and appear on the Japanese market. In such a case, there are also some cases that its design and trademark have been registered by a third party in the above region.
It will be too late to take measures against the imitation product by obtaining intellectual property rights for the toy in other countries when you have faced the situation where the imitation product has prevailed on the Japanese market. Thus, we strongly recommend you to file a design application in other countries at the same time as you obtain a design right in Japan. Please feel free to contact us if you would like to expand your business outside Japan.
Management of design rights differs among countries. For example, (i) Europe and the United states which are advanced countries in intellectual properties, (ii) East Asian and South East Asian countries and (iii) other countries each have their own practice and require their know-how about a manner to resister a design, and there are also measures other than applying design rights to protect designs. Having the experiences in the field of design rights, we are happy to support you.
Japan joined the Hague Agreement in 2015, which allowed us to file international design applications. With use of this system, it is possible to simplify registration procedures and reduce cost.
(6) "HARAKENZO more " support those in the toy industry
In the toy industry, companies intend to distinguish their products from others’ products by their own designs, and this can be their major strategies. Meanwhile, if designs for toys are not suitably protected with intellectual property rights, the designs are imitated and imitation products appear on the market easily. As a result, those in the toy industry will be forced to take measures against such imitation products.
There may be some cases where those in the toy industry will face a situation that forces them to deal with an issue of intellectual property rights. "HARAKENZO more " have established a system to provide thorough support for protecting intellectual properties of those in the toy industry. Please feel free to contact us.
意匠の疑問・お悩みはHARAKENZOに相談ください!

意匠登録や意匠トラブルの解決にあたっては、専門家の判断が欠かせません。
意匠のことでお悩みがありましたら、いつでも知的財産のプロフェッショナル集団であるHARAKENZO事務所にご相談いただけます。
